HTML Elements are the foundation of web pages. It defines the structure and layout of content in a web page. HTML element consists of an opening tag, content, and a closing tag. Some elements are self-closing.
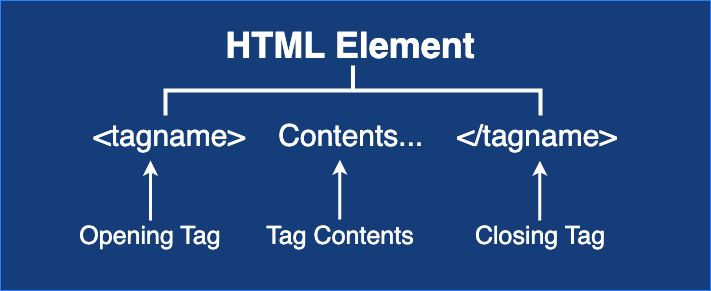
Syntax of HTML Element
<tagname> Contents... </tagname>For example:
<h1>Heading Content</h1>
<p>Paragraph Content</p>Here, <h1> and <p> are the opening tag, </h1> and </p> are the closing tag, and the text in between is the content.
Nested HTML Elements
HTML Elements can be nested means it can contain another HTML elements. In below example, <div> element contains two another elements i.e. <h1> and <p>.
<div>
<h1>Heading Content</h1>
<p>Paragraph content</p>
</div>Empty (or Void) HTML Elements
Some HTML elements does not contains ending tag, this type of tags are known as empty or void elements. For example – <hr>, <br>, <img>, …, etc.
HTML Elements are not Case Sensitive (Case Insensitive)
HTML elements can be used either in small letters or in capital letters. It is not case sensitive but it is recommended to use small letters. For example, <p> and <P> both are same.
Type of HTML Elements
HTML elements can be categorized based on their usage and behavior.
1. Structural Elements
These elements define the structure and layout of a web page.
<html>– It defines the root element of an HTML document.<head>– It contains meta descriptions, title, styles, and scripts.<body>–It contains all elements that are visible to the web page.<header>– It defines introduction content or navigation links.<footer>– It contains footer information like copyright or contact details.<section>– It defines the sections within a document.<article>– It is used for self-contained content.<aside>– It defines the side content, such as advertisements or widgets.<nav>– It contains the navigation links for website content easy access.<main>– It defines the primary content of a document.
2. Text Formatting Elements
These elements control text appearance and formatting.
<h1>to<h6>– It defines the heading content, where <h1> is the largest and <h6> is the smallest heading.<p>– It defines the paragraph content.<strong>– It is used to define the strong emphasis (bold) text.<em>– It represents the emphasized text (italicized).<span>– It is an inline container for styling the text.<br>– It is used to insert a line break.<hr>– It is used to create a horizontal line.<blockquote>– It is used to indicate a block of quoted text.
3. List Elements
List elements are used to organize contents in an ordered or unordered manner.
<ul>– It defines an unordered list (bulleted list).<ol>– It defines an ordered list (numbered list).<li>– It defines a list item within<ul>or<ol>.<dl>– It is used to create a description list.<dt>– It represents a term in a description list.<dd>– It represents a description of a term.
4. Link and Navigation Elements
These elements help users navigate between web pages.
<a>– It is used to create a hyperlink.<nav>– It contains navigation links.
5. Image and Media Elements
These elements are used to embed images, audio, and videos.
<img>– It is used to display an image.<audio>– It is used to embed an audio file.<video>– It is used to embed a video file.<source>– It is used to define multiple media sources.<figure>– It is used for groups media with captions.<figcaption>– It provides a caption for<figure>element.
6. Table Elements
Tables display structured data in rows and columns.
<table>– Defines a table.<tr>– Represents a table row.<th>– Defines a table header.<td>– Defines a table data cell.<caption>– Provides a title for the table.<thead>,<tbody>,<tfoot>– Groups rows within a table.
7. Form Elements
Forms collect user input through interactive controls.
<form>– Defines a form.<input>– Accepts user input.<textarea>– Allows multi-line text input.<button>– Creates a clickable button.<select>– Creates a dropdown menu.<option>– Defines options within<select>.<label>– Labels form elements.<fieldset>– Groups related form elements.<legend>– Provides a caption for<fieldset>.
8. Interactive Elements
These elements enhance user interaction.
<details>– Creates a collapsible section.<summary>– Defines a summary for<details>.<dialog>– Creates a modal dialog box.
9. Semantic HTML Elements
Semantic elements provide meaning to web content.
<article>– Represents self-contained content.<section>– Groups-related content.<aside>– Contains side content.<figure>– Encapsulates media content.<main>– Defines the main content.